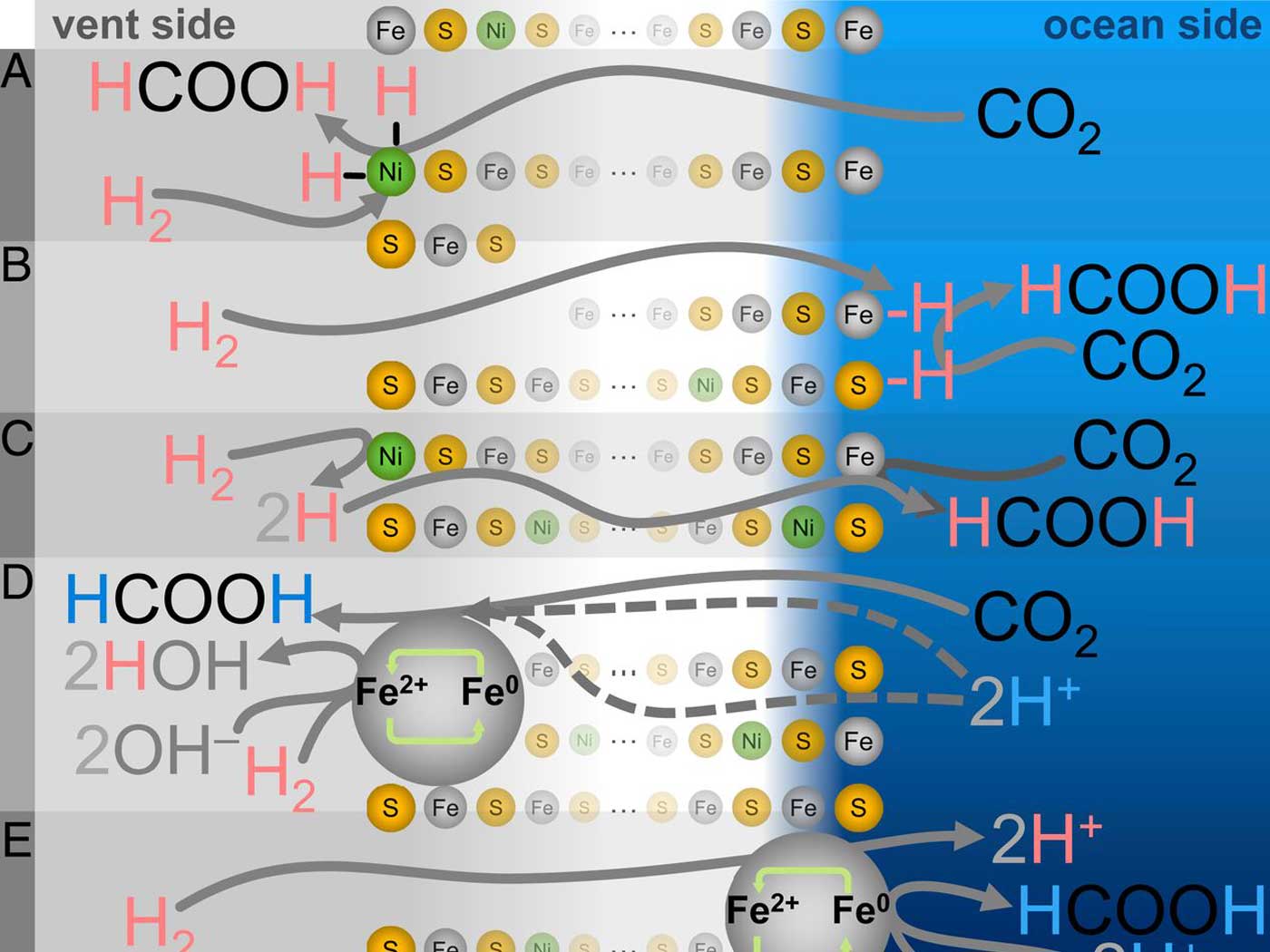
How would a vehicle slow or stop on time or on target without some mechanism to disengage the engine from the drive train?
The vehicles that transport items within living cells face the same challenges as vehicles that transport people and goods. One molecular vehicle inside cells uses a protein motor called dynein. And researchers just discovered that a detachable clutch-like protein regulates its speed.1
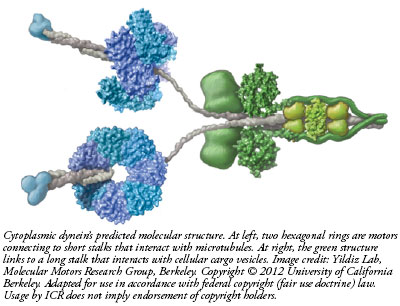 The dynein motor walks along microtubules, which are like train tracks inside cells. One end of the two-motor complex, which is a complex of 12 separately manufactured protein parts, has a long stem that acts like a trailer hitch attachable to a cargo bundle. At the other end, a short stalk connects to a pair of molecular leg-like appendages that alternately attach and detach as they literally walk down the length of a microtubule. This way, a cell transports products from one area to another. But what if there was no way to control how fast the dynein walked?
The dynein motor walks along microtubules, which are like train tracks inside cells. One end of the two-motor complex, which is a complex of 12 separately manufactured protein parts, has a long stem that acts like a trailer hitch attachable to a cargo bundle. At the other end, a short stalk connects to a pair of molecular leg-like appendages that alternately attach and detach as they literally walk down the length of a microtubule. This way, a cell transports products from one area to another. But what if there was no way to control how fast the dynein walked?
Without a clutch-like mechanism to regulate its speed, a cellular motor would carry its cargo too fast and too far, requiring constant cargo re-routing. Too much of such confusion would disrupt the cell's finely tuned and highly efficient inner workings. In short, failure to regulate the speed of protein motors could cause fatal intracellular traffic jams.
Fortunately, dynein motors are modulated by what researchers called a "clutch." A separate protein named "Lis1" attaches right where the appendages connect to the dynein's central motor. When the researchers added Lis1 to fully fueled dynein motors, they watched the dynein walking action slow down dramatically.2 The study authors reasoned that Lis1disrupts the connection between dynein motors and their walking appendages, much like a clutch disengages an automobile engine from the transmission.
The specified complexity of Lis1, which is exactly the right size, shape, strength, and charge to fit perfectly into its notch on the dynein complex and fulfill its purpose, is one of thousands of essential details that the Creator provided for living cells.
References
- Huang, J. et al. Lis1 Acts as a "Clutch" between the ATPase and Microtubule-Binding Domains of the Dynein Motor. Cell. 150 (5): 975-986.
- To do this, the researchers chemically bonded molecular markers onto the dynein complexes, so that specialized equipment could visualize the motors in a laboratory setting.
* Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Article posted on October 10, 2012.