Fossil discoveries in eastern Morocco’s Kem Kem beds have been fascinating paleontologists for decades. These sandy-rich units outcrop for a few hundred miles along the Algerian-Moroccan border in northwest Africa. The fossil-rich strata are claimed to be mid-to-early Late Cretaceous.2 Above the Kem Kem layers sits an extensive Late-Cretaceous limestone unit that covers much of North Africa.2 Below the Kem Kem are marine-fossil rich rocks of Devonian, Silurian, and Cambrian strata.2
Lead author Nizar Ibrahim, from the University of Detroit Mercy, and colleagues cataloged large theropod dinosaurs, sharks, bony fishes, and lobe-finned fishes, such as the coelacanth, turtles, crocodyliforms, pterosaurs, as well as invertebrate, plant, and trace fossils from the Kem Kem.2
“This is the most comprehensive piece of work on fossil vertebrates from the Sahara in almost a century, since the famous German palaeontologist Ernst Freiherr Stromer von Reichenbach published his last major work in 1936," wrote David Martill, of the co-authors of the study.1
Oddly, the scientists found that there seemed to be an abundance of large theropod (meat-eating) dinosaurs in the Kem Kem, too many to be easily explained.2 The study authors described:
The Kem Kem vertebrate fauna is biased toward large-bodied carnivores including at least four large-bodied non-avian theropods (an abelisaurid, Spinosaurus, Carcharodontosaurus, and Deltadromeus), several large-bodied pterosaurs, and several large crocodyliforms. No comparable modern terrestrial ecosystem exists with similar bias toward large-bodied carnivores.2
To explain the diversity of the fossil assemblages, the study authors acknowledged that the Kem Kem must “as a whole represent a “compound assemblage” derived from two formations (Cavin et al. 2010) or from disparate paleoenvironments (Dyke 2010).2
Does simple mixing of two formations explain the diversity of the fossils found in this unit, a unit sandwiched in between layers of marine rocks? And how do these uniformitarian scientists explain so many types of theropods in a single rock unit? Was this just a dangerous place to live, or is there another reason?
In 2015, we reported that Ibrahim had discovered car-sized coelacanths and other marine fossils in these same rock layers (the Kem Kem) along with a 50-foot Spinosaurus dinosaur.3,4 Today’s coelacanths live about 500 feet below the ocean surface and not in freshwater rivers as paleontologists insist that they did in the past, the present study included.2,3 The claimed mixing of rivers and delta environments still cannot explain the tremendous diversity of the fossils nor the predominance of large theropod dinosaurs found together in the same rock layer.
The global Flood offers a better explanation for what we observe, not only in the Kem Kem, but in the rock layers above and below also. According to ICR’s pre-Flood geographic interpretation, the western border of Morocco was likely the edge of a shallow sea, with some lowlands and uplands to the south and west.5 This explains the predominance of shallow marine fossils in the underlying formations; these animals were simply buried in the earliest part of the Flood as tsunami-like waves began to crash across the shallow oceans (Devonian, Silurian and Cambrian) rocks beneath the Kem Kem.
As the floodwaters rose higher in the Cretaceous, the waves washed over the lowlands and even the uplands, causing the large dinosaurs and other animals to congregate together on the remaining bits of drier land and/or shallowest water. This explains the unusual diversity of the fossil assemblage, including the many large theropod dinosaurs all found in close proximity. These animals were huddled together trying in desperation to survive. This truly was the deadliest moment in the history of the Earth.
Eventually, even the largest dinosaurs succumbed to the rising floodwaters and became entombed in the strata of the Kem Kem. Shortly thereafter, the sea rose even higher, reaching its maximum level at the end of the Cretaceous, inundating the entire globe, and leaving a massive limestone bed across North Africa and much of Europe in its wake. There was only one global Flood as recorded in the Bible that drowned and buried billions of fossils. And it left behind the carnage in the rock layers for us to observe today.
Finding dinosaurs mixed with marine fossils like coelacanths and sharks is commonplace in the rocks of the Flood from the United States to Brazil, from India to Morocco. Earlier, I had reached the same conclusion:
Dinosaur fossils found in rock strata with marine fossils are commonplace, not the exception. The fossil evidence supports a catastrophic and global flood that mixed the marine realm with the terrestrial realm as tsunami-like waves spread ocean fauna and sediments across the continents. Genesis 7 and 8 describe this process better than any secular scientist could imagine.3
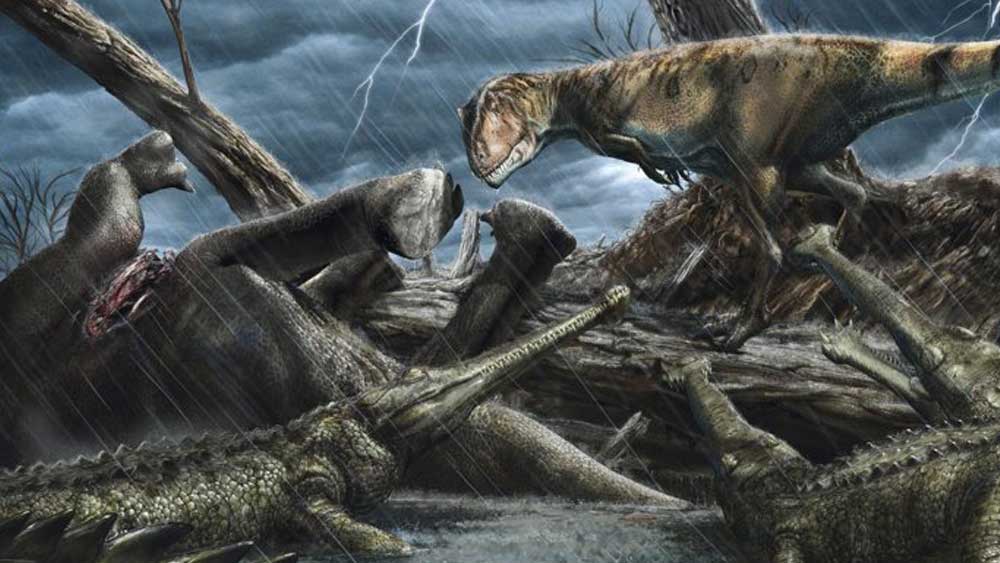
Stage image: A Carcharodontosaurus eyes a group of crocodile-like hunters called Elosuchus.
Stage image credit: Davide Bonadonna/ScienceAlert. Copyright © 2020. Adapted for use in accordance with federal copyright (fair use doctrine) law. Usage by ICR does not imply endorsement of copyright holders.
References
1. Dockrill, P. 2020. Palaeontologists Think They Have Found 'The Most Dangerous Place' in Earth's History. ScienceAlert. Posted on sciencealert.com April 28, 2020, accessed April 30, 2020.
2. Ibrahim N. et al. 2020. Geology and paleontology of the Upper Cretaceous Kem Kem Group of eastern Morocco. ZooKeys. 928: 1-16.
3. Clarey, T. 2015. Dinosaurs in Marine Sediments: A Worldwide Phenomenon. Acts & Facts. 44 (6).
4. Ibrahim, N. et al. 2014. Semiaquatic adaptations in a giant predatory dinosaur. Science. 345 (6204): 1613-1616.
5. Clarey, T. 2020. Carved in Stone. Dallas, TX: Institute for Creation Research, 400-417.
*Dr. Clarey is Research Associate at the Institute for Creation Research and earned his doctorate in geology from Western Michigan University.